Digital engineering
We increase company productivity, find and optimize bottlenecks and inefficient aspects in production, logistics and business processes, develop technological solutions.


We increase company productivity, find and optimize bottlenecks and inefficient aspects in production, logistics and business processes, develop technological solutions.
The topic is complicated, so let's talk about it in order.
In simple words: we come into the company, analyze your business processes, find the most problematic aspects and offer to deal with them using digital technologies, rather than classical advice like hiring more employees and opening additional sales offices.
Benefits in effective problem solving:
Digital engineering does not imply a typical solution for everyone; it improves the benefit and unique advantage.
👉 Another important thing. If you extend your business with standard means: increase your staff, buy more equipment that is the risk to increase hidden problems. There are always hidden problems because the longer a company exists, the more complicated it is - and entropy increases with time. Digital engineering helps to cope with it, making all the hidden processes transparent.
We ourselves work on the principles of digital engineering through HR and financial management systems.
Just like this:
One more time:
A large factory producing 10,000 parts per day. Because it already has a department of specially trained people.
Company in crisis, in debt, and in flames. We cannot help because digital engineering is not an anti-crisis program, but a special benefit magnifier that works when there is money for it.
Vegetable stand. Because the cost of our work will be greater than the benefit it can get.
A delivery company that delivers 20-30 orders a day. Because digital engineering is expensive and standard solutions can work instead of it in this case.
A plant with a small management staff, where all major decisions are made by the director.
A stable company that produces a stable result, but wants to grow and has money for it.
A network of 50 vegetable stands with warehouses, large assortment, and its own logistics.
Logistics companies delivering 1500 orders per day.
The process consists of 4 steps.
1. Analysis. We look into the work of the company: we study what is going on, what business processes exist, we figure out who is responsible for what, we look for bottleneck areas, we ask many questions. Usually, it takes from 1 month to 3 months.
Often a company may lack a simple and detailed description of business processes. This is the most obvious benefit.
2. Problem and solution. Based on the results of the first step, we find a solution that will bring tangible benefits to the company. A typical problem of any commercial company is the fragmentation of all received data and misunderstanding of the full picture of business processes. That's because:
We try to integrate solutions gently so as not to break down existing processes.
We release a pilot version3. Pilot run. At this step, we test our solution and test its performance. This is a necessary step, which is necessary to confirm the correctness of the chosen solution and to plan the next step in real conditions. If everything is okay - we continue integration, if there are difficulties or the solution does not work at all - we fix the solution with minimal costs for the company.
A pilot decision can fail, it happens. If in the course of our work we all realized that the solution is nothing, it is also the result. Yes, it's expensive and losing a lot of money hurts, but it's a risk. So in the next step, we will find a more appropriate solution.
This is usually due to over-expectations, unannounced systemic problems in production or a large number of unknowns. In any case, even if it fails, the pilot helps identify undetected problems so that they can be solved later. It's unpleasant, but you should be prepared for it. And, of course, we talk about it before the contract is signed.
Getting to the next step4. Next step. Based on the previous work, we offer the next step of optimization.
The work is paid for and planned in steps, so if, for example, after the second step you understand that you cannot proceed - you pay for the work done, and that's it.
Your personal manager keeps you informed and is always in touch throughout the work.
We combine all services into a single information system
We combine all services into a single information system. It is when all services of the company (1C Accounting, site on Bitrix, excel files) work in one digital space. By default, they are not connected to each other. Accounting department works with its information, a certain specialist is responsible for excel files, storekeepers live in their world, the mechanic is responsible for car maintenance. We make it so that the information is collected in one system, so you can already work with it.
Further on, we connect the financial planning, logistics and decision making modules to this system. The modules are programs to analyze all the incoming information: seasonality, production history, sales history, scheduled repairs, probable errors - and build a plan of the enterprise, delivery routes and predict risks and solution options.
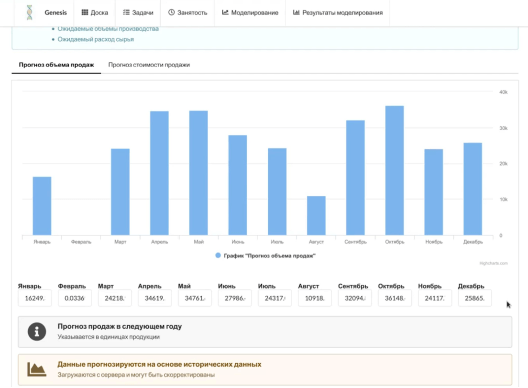
Sales forecast based on the previous years' data
We developed three modules and they are similar to the company departments:
For example, you're the director of a food-film company. We combine all services in one system, modules analyze the data and make an annual financial forecast. From this forecast it becomes clear that all previous 5 years in May you ordered 3 times more products than usual, but the company did not cope with it and gained more than it can give by the right time.
The situation is likely to repeat this year, which means that this is a bottleneck and needs to be worked on: pre-order raw materials, find additional employees and make sure that the machines do not fail at the wrong time.
So modules form tasks for buyers, human resources, storekeepers and so on, and you, as the head of the company make the final decision. If the promised peak of orders does not occur (there is always a probability), the decision-making module helps to get out of the situation with the least losses.
We make applications, create devices
We make applications, create devices. We write programs to help solve the problem.
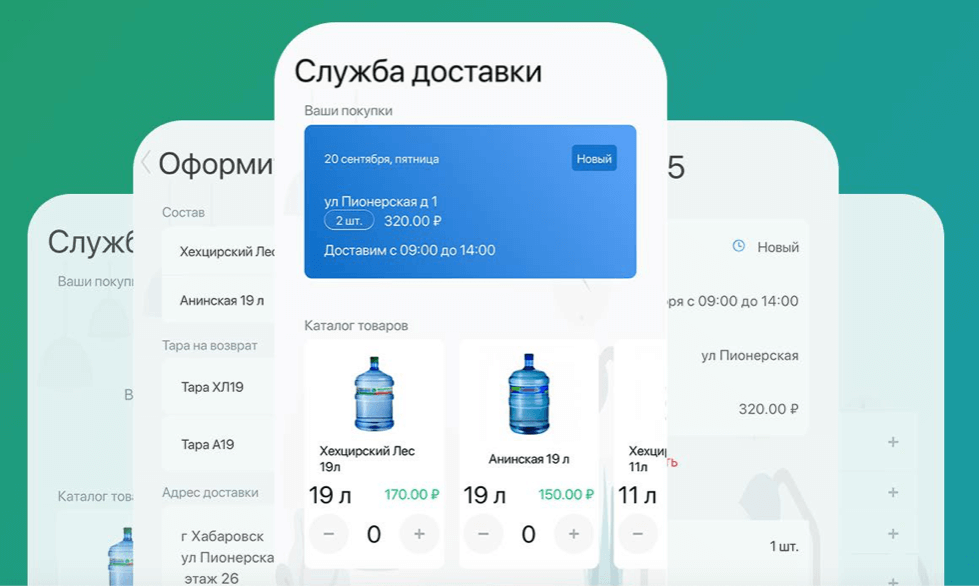
Route building application that runs on Google maps
For example, for a delivery company, we have written 2 types of applications: for teams and clients. Teams look at their route; see further orders, statistics, can accept payment directly through the application. A client orders the goods, watches the expected time of delivery and can pay with the card through the smartphone of the delivery agent.
Besides, we create the necessary devices and sensors. But, if it turns out that there is already a cheaper analog on the market, we will advise to use it. You can learn more about this in the article about turnkey projects.
We create a digital copy of the enterprise
We create a digital copy of the enterprise. These are virtual copies of production lines, which predict more accurate and efficient forecast of activities and help save money. For example, they can simulate what happens if you increase output on the lines or change the process chain. This is possible by processing data that is collected from finance and planning programs, machine tool probes and cameras at the workplace.
We combine all services into a single information system. It is when all services of the company (1C Accounting, site on Bitrix, excel files) work in one digital space. By default, they are not connected to each other. Accounting department works with its information, a certain specialist is responsible for excel files, storekeepers live in their world, the mechanic is responsible for car maintenance. We make it so that the information is collected in one system, so you can already work with it.
Further on, we connect the financial planning, logistics and decision making modules to this system. The modules are programs to analyze all the incoming information: seasonality, production history, sales history, scheduled repairs, probable errors - and build a plan of the enterprise, delivery routes and predict risks and solution options.

Sales forecast based on the previous years' data
We developed three modules and they are similar to the company departments:
For example, you're the director of a food-film company. We combine all services in one system, modules analyze the data and make an annual financial forecast. From this forecast it becomes clear that all previous 5 years in May you ordered 3 times more products than usual, but the company did not cope with it and gained more than it can give by the right time.
The situation is likely to repeat this year, which means that this is a bottleneck and needs to be worked on: pre-order raw materials, find additional employees and make sure that the machines do not fail at the wrong time.
So modules form tasks for buyers, human resources, storekeepers and so on, and you, as the head of the company make the final decision. If the promised peak of orders does not occur (there is always a probability), the decision-making module helps to get out of the situation with the least losses.
We make applications, create devices. We write programs to help solve the problem.

Route building application that runs on Google maps
For example, for a delivery company, we have written 2 types of applications: for teams and clients. Teams look at their route; see further orders, statistics, can accept payment directly through the application. A client orders the goods, watches the expected time of delivery and can pay with the card through the smartphone of the delivery agent.
Besides, we create the necessary devices and sensors. But, if it turns out that there is already a cheaper analog on the market, we will advise to use it. You can learn more about this in the article about turnkey projects.
We create a digital copy of the enterprise. These are virtual copies of production lines, which predict more accurate and efficient forecast of activities and help save money. For example, they can simulate what happens if you increase output on the lines or change the process chain. This is possible by processing data that is collected from finance and planning programs, machine tool probes and cameras at the workplace.
As you've already learned, it's an expensive service. We usually tell our clients that the entry threshold starts at 10 million RUR, but it can still be smaller because digital engineering is done in steps. If you get enough analysis and description of processes as a result of the first one, you will pay only for this part of work.
If you allocate 25 millions RUR for this service, you can apply for a subsidy from the Industrial Development Fund . In some cases it reaches 50%.